Category: Pharmacy
-
2.2 Controlled Substances
Each controlled substance is categorized by its addictive potential and risk of abuse Technicians should know each schedule and the…
-
4.1 Your Guide to Nonsterile Compounding Techniques

Not all medications dispensed in the pharmacy are tablets and capsules, some need to be prepared in the pharmacy Non-sterile…
-
1.9 Incompatibilities in Nonsterile Compounding

As technicians, we may need to compound medications for specific patient needs and care As we compound it’s important to…
-
3.2 Error Prevention Strategies

In the pharmacy, errors can lead to dangerous outcomes Accidentally switching one medication for another can cause an adverse event…
-
4.4 NDCs, Lot Numbers, and Expiration Dates

Believe it or not, those long numbers on the front or side of the bottle designate important information about each…
-
3.3 Bandwidth of the Pharmacy Technician

A patient comes up with a new prescription in hand asking you, the technician, if it has to be taken…
-
4.2 Sig Codes for Pharmacy Technicians

You receive a prescription that reads “Lipitor 10 mg i po qhs 30d NRF.” From this mix of abbreviations and…
-
1.2 Therapeutic Equivalence

If you’ve already started studying for your technician exam, and chances are you are well aware of the generic and…
-
1.10 Proper medication Storage

It’s Tuesday morning and the medications from your distributor just arrived, your task? Stock the shelves You pull out insulins,…
-
4.2 Unit prefixes and conversions for pharmacy technicians
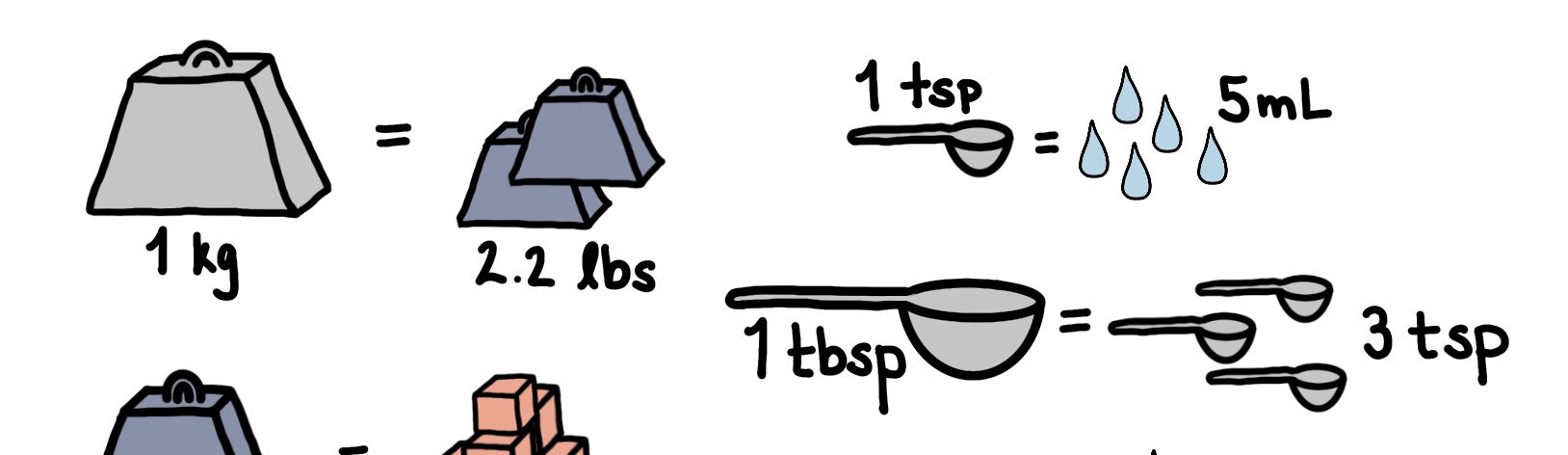
You receive a prescription from the doctor, it’s for 500mg of Levetiracetam solution taken B.I.D. The stock bottle lists 100…
